The automotive industry is undergoing significant transformation. Automotive Injection Molding plays a crucial role in manufacturing components. It contributes to lower costs and enhanced efficiency. Recent reports indicate that the global automotive injection molding market is projected to reach $36 billion by 2024. This growth underscores its importance in vehicle production.
However, not all techniques are created equal. Each method has its own advantages and limitations. This can lead to challenges, such as quality inconsistencies and production delays. Despite these issues, innovative techniques are emerging. Companies are constantly exploring ways to optimize processes and reduce waste.
Understanding the top injection molding techniques is essential for manufacturers. It can determine the success of parts production. A comprehensive grasp allows engineers to select the best methods for specific applications. As the automotive landscape evolves, embracing efficient injection molding is not just beneficial—it's imperative.
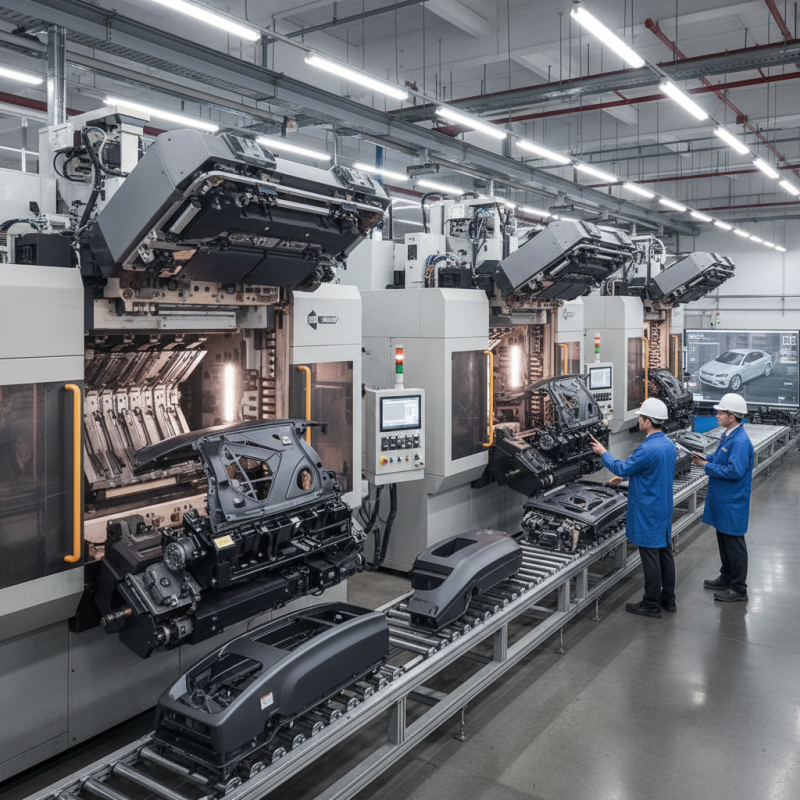

Automotive injection molding is a key process in vehicle production. It allows for the creation of complex parts quickly and efficiently. Various techniques are used in this domain, each with unique advantages. The most common includes thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. These materials can be molded into different shapes under pressure. This versatility helps meet the diverse needs of the automotive industry.
While the benefits are clear, some challenges persist. For example, achieving precision in mold design is critical. A small error can lead to defective parts. Another concern is the environmental impact of plastic waste. Recycling initiatives are still developing. It’s essential to explore alternatives and embrace sustainability.
Another aspect worth mentioning is the speed of the molding process. Quick production times can lead to errors if not monitored properly. Continuous improvement is needed to enhance quality control. Companies must remain vigilant in testing and monitoring. The balance between efficiency and quality is delicate. Understanding these nuances will drive better practices in automotive manufacturing.
Thermoplastic injection molding is a vital process in the automotive industry. This method involves melting plastic pellets and forcing them into molds. The result? Precise and durable automotive parts. The versatility of thermoplastics allows for a range of applications, from dashboards to exterior components.
The molding process is not without its challenges. Temperature control is crucial to achieve the right consistency. If temperatures are too high or too low, defects can occur. Each stage of production requires careful monitoring. Moreover, the recycling aspect of thermoplastics presents both opportunities and dilemmas. Innovations are needed to improve recycling efficiency and reduce waste.
Engineers often explore different thermoplastic varieties to find the most suitable match for specific applications. As they delve deeper, issues like strength and flexibility arise. Balancing these properties can be tricky. Continuous experimentation shapes the future of automotive design, yet the journey is filled with trial and error.
In automotive injection molding, various materials play a crucial role in the production of auto parts. One popular choice is thermoplastics. They are lightweight and versatile. Polypropylene is a common thermoplastic due to its strength and resistance to chemical exposure. It can withstand harsh automotive environments, making it ideal for interior and exterior components.
Another commonly used material is thermosetting plastics. These materials provide superior durability. They are often used in applications requiring heat and chemical resistance. For example, epoxy resins are ideal for structural components due to their strength. However, these materials have a longer curing time, which can complicate the production process.
Additionally, composites are gaining popularity in the automotive industry. They blend different materials to optimize performance. Fiberglass-reinforced plastics are lightweight and strong. However, achieving the right mix can be challenging. Each type of material has its pros and cons. Choosing the right one requires careful consideration of the part's requirements. This can lead to mistakes if not properly assessed.

Gas-assisted injection molding is a revolutionary technique in automotive manufacturing. It reduces material usage while enhancing part strength. The process involves injecting gas, usually nitrogen, into the mold simultaneously with the molten plastic. This creates a hollow section in the component. As a result, it decreases the weight of the part and improves fuel efficiency.
Two-shot molding offers a different approach. It allows for the creation of multi-colored and multi-material parts in a single cycle. This technique is particularly effective for components requiring different textures or hardness levels. The process involves a two-step injection sequence. The first material is injected, followed by a second material that bonds to the first. However, aligning the two materials perfectly can be challenging. Any misalignment can lead to defects.
Both techniques illustrate advanced capabilities in automotive manufacturing. Yet, they also demand precision. Manufacturers must constantly refine their processes. Minor flaws can have significant impacts. The industry must keep evolving to address these challenges.
Quality control is crucial in automotive injection molding. The rise of advanced technologies has improved processes significantly. However, challenges remain. Recent studies indicate that up to 30% of molded parts may not meet quality standards. This can lead to costly recalls and damaged reputations.
Efficiency also plays a key role. According to industry reports, companies that implement rigorous quality assurance measures can reduce waste by 25%. Streamlined processes increase speed without sacrificing quality. However, many manufacturers struggle with balancing these aspects. It’s a delicate dance between cost, speed, and quality control.
Innovations like in-line monitoring systems are helping manufacturers. These systems detect defects in real-time. Yet, there’s still a reliance on manual checks in many facilities. This often leads to inconsistencies. A recent survey showed that 40% of operators believe training is inadequate. This gap can hinder overall efficiency, calling for serious reflection and improvement in training protocols.
| Technique | Description | Key Benefits | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Injection Molding | A traditional method where melted plastic is injected into a mold. | High precision, versatility, and efficient production. | Engine parts, dashboards, interior components. |
| Gas-Assisted Injection Molding | Incorporates gas to reduce weight and improve structure. | Lighter parts, reduced material usage, fewer sink marks. | Housings, automotive frames, large sections. |
| Multi-shots Molding | Uses multiple injections to create multi-material parts. | Color variations, diverse material properties in one piece. | Handles, dashboards, custom designs. |
| Insert Molding | Involves placing inserts within the mold before injection. | Enhanced durability, complex assembly, reduced assembly costs. | Electrical components, reinforced parts. |
| Blow Molding | Creates hollow plastic parts using air pressure. | Efficient for large volumes, reduces labor costs. | Fuel tanks, containers, ducts. |
| Rotational Molding | Involves heating and rotating the mold to distribute plastic. | Uniform thickness, large components, minimal waste. | Large automotive parts, storage tanks. |
| Thermal Molding | Uses heat to form plastic into shapes. | Flexibility with materials, quick set-up time. | Custom components, flexible parts. |
| Compression Molding | Forces material into a mold under heat and pressure. | Efficient for large parts, good for rubber and plastics. | Seals, gaskets, automotive interior parts. |
| Foam Injection Molding | Creates foam structures for lighter components. | Reduces weight, improves insulation qualities. | Door panels, seat backs. |
| 3D Printing and Injection | Combines 3D printing with traditional injection methods. | Customization, rapid prototyping, complex designs. | Prototypes, custom tools. |