Injection Molding Material Guide: Exploring the Main Materials & Plastics
Injection Molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity to create precise, complex shapes used in various industries—from automotive to consumer goods. In this guide, we’ll explore the main types of materials and plastics commonly used in injection molding, including Polyethylene (PE), Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE), Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), and others.
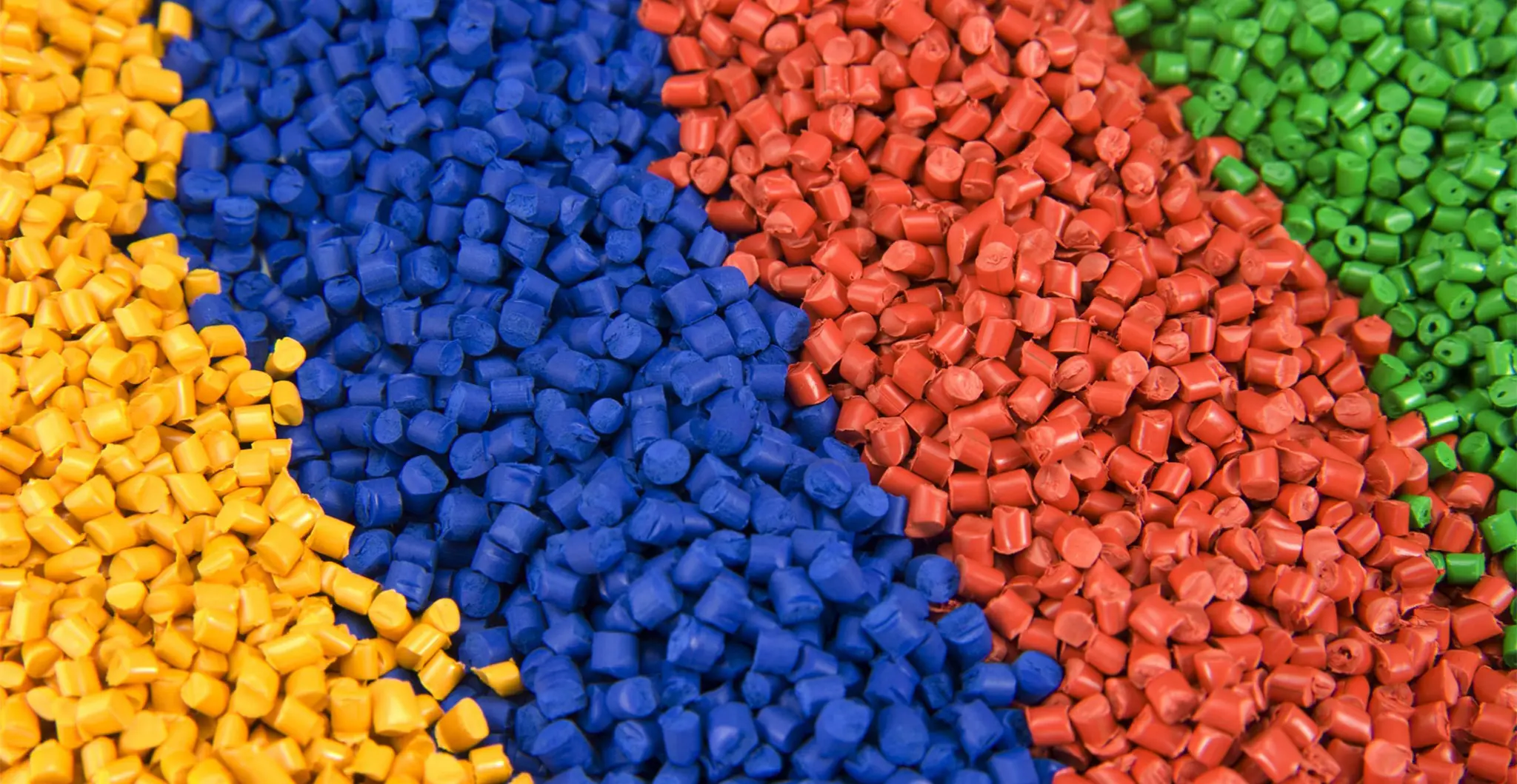

1. Thermoplastics: The Most Common Injection Molding Material
Thermoplastics are by far the most widely used materials in injection molding. They can be melted and re-solidified repeatedly without significant degradation, undergoing major damage, making them ideal for mass production and very economical.
Polyethylene (PE): Polyethylene is one of the most widely used plastics due to its excellent chemical resistance, low friction, and flexibility. It has different grades, including High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). PE is commonly used for containers, toys, plastic bags, and piping systems.
Polypropylene (PP): It is a common material for automotive components, storage containers, and medical instruments owing to its incredible chemical resistance and longevity but more importantly low cost; such attributes save a lot in investment.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS boasts many wonderful characteristics such as toughness with high-impact resistance, good shaping properties in numerous applications from parts for appliances and automobiles to toys and household products.
Polystyrene (PS): This is a rigid, brittle plastic that is easy to mold. It is commonly used in many disposable items like plastic cutlery, food packaging, and electronic housings.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): PET is a highly durable and versatile plastic, well-known for its clarity, strength, and chemical resistance. It is a popular choice in a wide array of applications, including bottles, containers, food packaging, and textiles. PET is often chosen for its ability to withstand both high and low temperatures without warping or cracking.
2. Thermoplastics Elastomers (TPE): Versatile and Flexible
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are rubber-like materials that provide the flexibility of elastomers with the moldability of thermoplastics. TPEs are increasingly popular in industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods.
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers): These materials offer flexibility, durability, and excellent stress-crack resistance, making them ideal for applications like automotive seals, medical devices, and consumer products such as soft-touch grips, footwear, and phone cases. TPE is highly recyclable and can be used to produce products that require rubber-like properties but are easier to process compared to traditional rubbers.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): TPU belongs to the class of polyurethane plastics and has high abrasion resistance, flexibility, and is resistant to oils and greases. TPU is commonly used in applications like sporting goods, footwear, automotive parts, and medical devices. Additionally, TPU’s excellent layer adhesion and flexibility also make it a popular choice as a filament for 3D printing, allowing the creation of intricate and durable objects across a multitude of fields.
3. Engineering Plastics: For High-Performance Applications
Engineered plastics are designed to withstand extreme conditions, including high heat, pressure, and heavy loads. These materials are ideal for applications requiring strength, durability, and stability.
Nylon (Polyamide): Nylon is one of the most versatile engineering plastics, offering excellent wear resistance, toughness, and dimensional stability. It's used in automotive components, electrical connectors, and industrial machinery parts.
Polyoxymethylene (POM): Also known as acetal, POM offers low friction, high stiffness, and good wear resistance. It's used in gears, bearings, and other mechanical components.
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS): PPS is known for its high heat resistance and dimensional stability. It's used in automotive and electrical applications that require high performance in extreme conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Injection Molding
In summary, this comprehensive guide delves into the key materials used in injection molding, highlighting their distinct properties and suitability for various applications. Each material, from thermoplastics to elastomers, offers unique advantages in terms of durability, flexibility, and resistance to heat and chemicals. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for selecting the right material to achieve optimal performance.
By understanding these material properties, injection molding manufacturers like DX Mold can make informed, strategic decisions, ensuring the functionality, reliability, and quality of their products.